Key takeaways
- Staking Ethereum involves locking coins in the network to validate transactions and earn rewards.
- Before starting the staking Ethereum process, you should learn the key concepts, including Ethereum proof-of-stake, validators, epochs, slashing and staking pools.
- To maximize Ethereum staking rewards, you can consider using up-to-date hardware, choosing reliable platforms and reinvesting earnings.
- The easiest way to start staking is to join a staking pool via a reliable crypto exchange or platform.
Staking Ether (ETH) allows you to put your crypto to work without the risks of trading or investing in speculative tokens. With Ethereum’s move to become a proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain, anyone can now start staking to secure the network and earn rewards.
This Ethereum staking guide breaks down everything you need to know, including key technical terms and step-by-step instructions on how to get started.
Why stake Ethereum? Benefits of ETH staking
For a blockchain to operate securely, independent participants must verify transactions honestly.
On Ethereum, this is done via a consensus method called PoS. Users must lock their ETH coins to the network to become a validator node and process transactions.
So why would anyone decide to stake Ethereum?
- Passive income: Users are rewarded for staking their cryptocurrency on the network. In return for their commitment and validating transactions, they are paid rewards. On Ethereum, this is around 3%. It helps long-term holders earn extra passive income, similar to earning interest on your funds.
- Network security: Staking ETH helps to secure the network, as the more users acting as validators on the network, the more robust and harder it becomes to attack.
Did you know? On Sept. 15, 2022, the Ethereum blockchain transitioned from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake. The complex process enabled the network to be more energy-efficient and operate faster.
How Ethereum staking works: Key concepts
Before you start learning how to stake Ethereum, there are several technical terms you need to know:
- Proof-of-stake: PoS requires network validators to show their commitment by locking or ‘staking’ to the network. Validators must stake 32ETH, and in return, they can be randomly selected to propose and validate new blocks. Once validated, the new block is added to the blockchain.
- Validators: Validators are individuals or entities that stake ETH to process transactions and create new blocks.
- Epochs: An epoch is a measure of time it takes validators to complete the actions of proposing and attesting to new blocks. On Ethereum, this is fixed to 32 slots of 12 seconds, so an epoch is 6.4 minutes.
- Slashing: This occurs when a validator breaks a network rule. Penalties are imposed on anyone who acts maliciously and fails to validate transactions correctly. Penalties include reducing ETH balances and removal for active validation.
- Staking pools: Groups of people can combine their funds to afford the minimum staking requirement of 32 ETH or to increase their chances of being selected as validators to earn rewards. Rewards are then shared among the pool based on the amount contributed.
Did you know? Peercoin was the first PoS blockchain, and a white paper in 2012 introduced the concept as a solution to Bitcoin’s energy-hungry mining process. The network launched in 2013, demonstrating reduced power usage and making PoS a popular technology in future blockchains.
Maximizing your ETH staking rewards: Tips and best practices
While staking ETH, there are several ways you can improve your financial returns and guard against costly penalties:
- Correct hardware: To become a solo validator, you’ll need specific hardware, including a fast CPU, at least 16GB of RAM, 1TB SSD drive and 25MB/s bandwidth. Incorrect hardware could stop you from fulfilling validator duties efficiently and cost you some or all of your stake.
- Increase stake: Staking more ETH increases your chances of being chosen as a validator. Or, if you are using a staking pool, it increases your share of the rewards.
- Reliable platforms: If you decide to stake through a pool or “staking as a service” (SaaS) platform, make sure to choose a trustworthy operator. Do your research to avoid scams and poor service providers, which could risk your funds.
- Monitor performance: Check your validator’s performance and uptime to ensure you’re never missing out on rewards or being penalized for breaking the rules.
- Reinvest: Compound your passive income with Ethereum by staking your rewards.
Did you know? Ethereum is a hard fork of Ethereum Classic. Ethereum was forked from Ethereum Classic in 2016 after attackers exploited issues in the smart contracting code of “The DAO” project. The community implemented the hard fork to roll back transactions to allow lost funds to be recovered.
7 steps to start staking Ethereum and earning rewards
There are two ways to earn rewards staking ETH:
- Solo staking: You set up and run a validator node yourself. This requires investment in the correct hardware, technical knowledge and 32ETH.
- Staking pool: Join other stakers via a staking platform. The pool operator takes care of the hardware and management. You can deposit a small amount of ETH to get going. Many well-known exchanges now offer this service within their platforms.
Ethereum staking steps:
Step 1: Set up a secure wallet for staking
You’ll need an Ethereum-enabled wallet where you can store and manage your funds for staking. Hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor are considered secure options to store and manage funds.

Step 2: Get Ethereum (ETH)
If you don’t own ETH, you’ll need to buy some from a reputable exchange or provider. This can also be done directly inside your hardware wallet. For example, Ledger offers the option to buy ETH and deposit straight into your wallet.

Step 3: Choose your staking method
Now, you can choose your staking method, either solo staking or joining a pool. For illustration purposes, this article explains how to join and use Coinbase’s staking platform. It’s the straightforward way to get started.
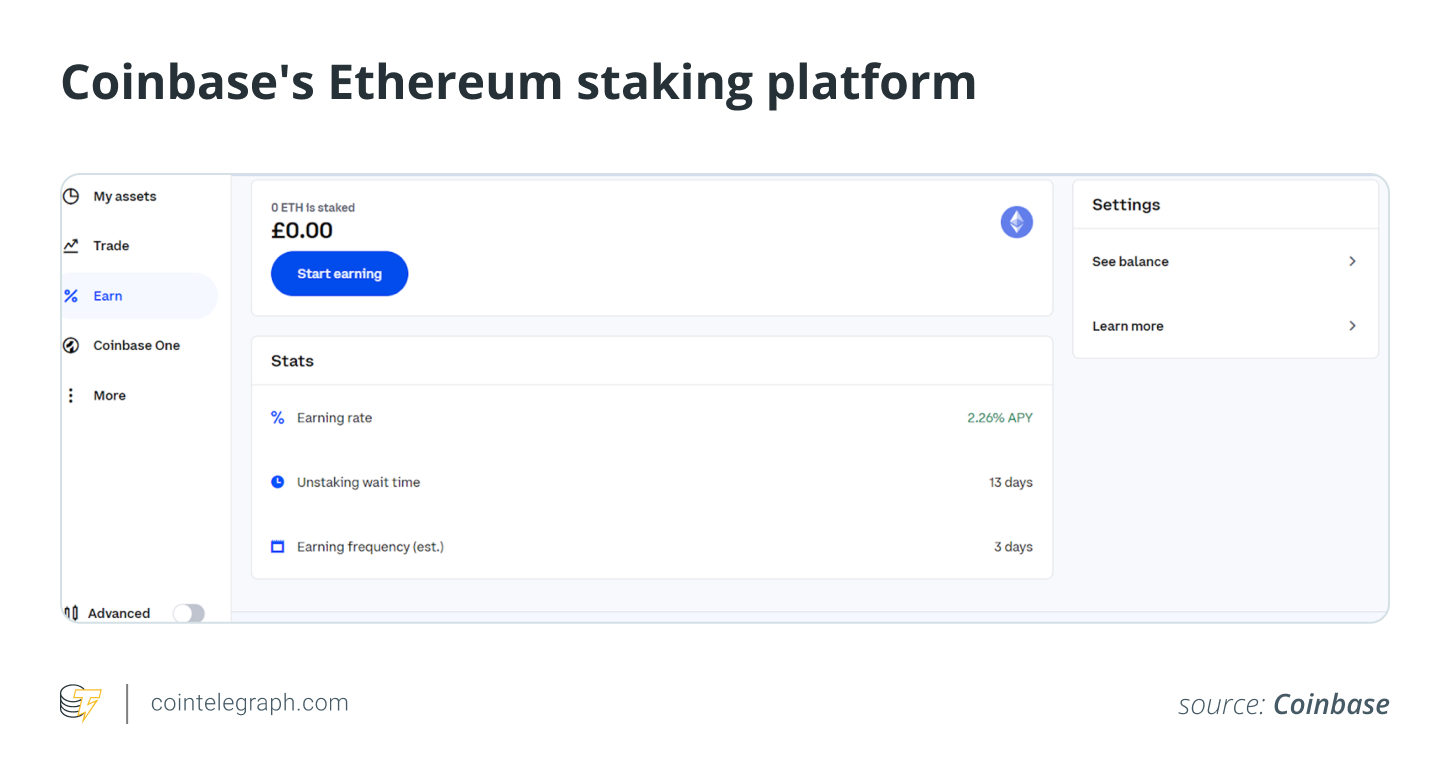
Step 4: Deposit your Ethereum for staking
Create and verify a Coinbase account. Then, you can create an Ethereum address and send ETH from your wallet to your Coinbase account.

Step 5: Start staking Ethereum
Navigate to the “Earn” tab on the Coinbase website or app. Select Ethereum, enter the amount you’d like to stake, and click “Stake Now.”

Step 6: Track your staking rewards
Navigate to Ethereum in the “My Assets” tab. On the right-hand side, you’ll see “My Earnings,” which shows your rewards and ROI. Ethereum staking rewards in 2024 are around 3%.
However, staking rewards may differ based on network conditions and several other influences. For example, validators using MEV-boost generally achieve an average return of approximately 5.69%. MEV-boost is an open-source tool used by validators to tap into a competitive marketplace for building blockchain blocks.

Step 7: Withdraw and reinvest your Ethereum staking rewards
Ethereum staking rewards are automatically added to your Coinbase account. You can then decide whether to reinvest or withdraw your earnings.
Regardless of the straightforward process, please be aware that staking involves risks such as losing assets due to validator issues, slashing penalties and network vulnerabilities.
Staked tokens can also be illiquid during lock-up periods, and market volatility may reduce rewards. It’s crucial to research thoroughly before participating to understand these risks.
Written by Marcel Deer
This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risk, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision.


